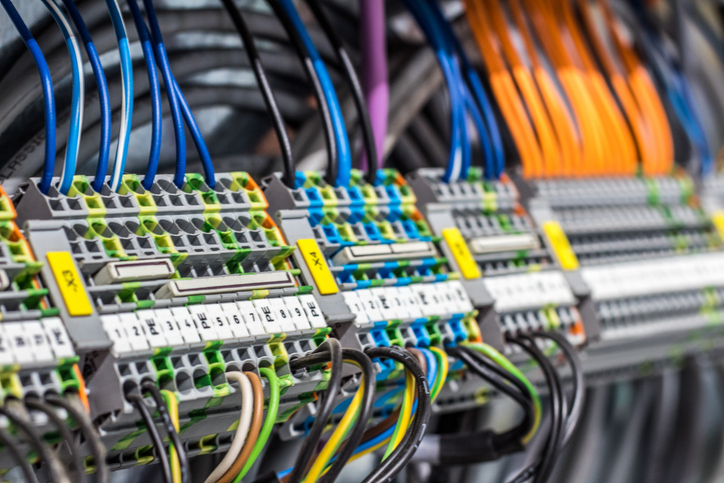
SIS Wire Specifications: The Details of Switchboard Wire
SIS (Switchboard Instrumentation and Switchgear) wire is a versatile wire used for many different electrical and switchboard cable applications. SIS is a go-to wire option in tough environments that call for a safe, durable, reliable wire option.
If you're in the process of selecting SIS for your application, it's important to understand the details like composition, standards, and ideal uses. Here, we break down the details of one of the strongest wire options on the market.
How is SIS Wire Used?
SIS wire is primarily used in switchgear and switchboard assemblies. Switchgear systems are used for the control and protection of industrial and commercial electrical equipment. It's used in many utilities and holds up to high voltage applications. It has superior insulation properties, is heat and abrasion-resistant, and is ideal for switchboard use.
Another common use of SIS wire is in control panel wiring for electrical equipment such as pumps, motors, and HVAC systems. Again, this is due to the ability to insulate and withstand high temps. SIS wire is flexible and easy to install in panel layouts as well.
SIS is rated for high voltage—typically 600v, making it a good option for power distribution applications in the electrical industry, where it carries electricity from the main source to machinery and subpanels. It's also a preferred wire selection for internal connections within transformers. The most demanding electrical applications and conditions call for a wire that can handle the temperatures and voltage.
You may also find SIS wire in sensitive instrumentation wiring and control systems. The excellent insulation ability prevents distortion and signal loss in monitoring systems, sensors, and measurement devices.
SIS wire is prevalent in electrical substations and industrial control panels used for power generation and distribution, lighting and building systems, and many other industrial applications. Any endeavor that calls for high-voltage capacity, flame retardance, durability, and flexibility is a good fit for SIS wire. The durable wire is even well-suited for marine and offshore environments—powering equipment on oil rigs and ships.
What Makes SIS So Durable?
Why is SIS so durable and rugged? It has the right material composition to handle the jobs it faces. There are several commonly used materials found in switchboard wires, including aluminum and copper.
- Tinned Copper: Tin plated copper is the go-to material for switchboard wiring because it's highly conductive, cutting back on energy loss and promoting efficiency. Stranded tinned copper conductors are durable and resist corrosion, wear, and tear, especially due to the tin coating, which also makes it easier to solder. The flexible nature of copper makes it easy to work with and install, even in areas with tight tolerances, such as switchboard and control panel setups.
- Aluminum: Aluminum wire is less conductive than its copper counterpart, but it's a lightweight, cost-effective SIS wire choice. The drawback of aluminum is that it’s prone to thermal expansion and oxidation. A larger gauge may be required (compared to copper wire) to achieve the right levels of conductivity.
- Insulation: Most SIS wire has cross-linked polyethylene insulation (XLPE), which is especially ideal for high-temperature environments. XLPE is durable and offers excellent electrical insulation. Other insulation materials that might be used in SIS include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), Silicone Rubber, and EPDM—a synthetic rubber material. Teflon insulation and neoprene insulation options may be selected for applications that need high-temperature stability or chemical resistance.
Voltage & Current Ratings for SIS Wire
SIS wire carries ratings for different voltages and currents. It's critical to choose an appropriate voltage and current-rated wire to ensure your wire can handle the application without overheating and causing equipment failure.
When selecting SIS wire, there are two numbers to review: voltage rating and ampacity (also called current rating). The voltage rating tells you the maximum voltage a wire can carry safely. SIS wire typically carries a voltage rating of 600v. It’s important to make sure that the rating matches the specifications of your system.
Current rating, or ampacity, is another number that tells you what a wire can handle. The ampacity refers to the maximum current (amperes) a wire can carry before the insulation is damaged. It depends on the ambient temperature of the application, the wire gauge, and the insulation type. Adequate ampacity prevents overheating and fire, so it’s vital to the safety of your application.
The best way to determine your correct wire needs is to check the NEC guidelines for voltages, along with any relevant industry standards. If you have questions about the capacity of any wire product, don't hesitate to contact our team at IEWC. Our wiring experts will help you make sure you have the ideal selection for the job.
What are the Industry Standards for SIS Wire?
When you choose SIS wire for your various applications, you want to make sure that it is compliant with all industry standards. These standards come from IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), NEC (National Electric Code), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), and UL (Underwriters Laboratories).
For SIS wiring, some of the key standards and certifications include:
UL44: Standard for Thermoset-Insulated Wires and Cables
This standard sets the requirements for thermoset insulation materials for voltage, temperature, and flame resistance, ensuring safety in electrical applications.
UL758: Standard for Appliance Wiring Material
This UL standard outlines the requirements for appliance electrical wires, including the guidelines for materials, construction, and performance.
ASTM B3: Conductor Standard for Soft or Annealed Copper Wire
The B3 standard ensures copper wire is suitably conductive, flexible, and durable when used in SIS applications.
ASTM B33: Standard Specification for Tinned or Annealed Copper Wire for Electrical Purposes
Similar to ASTM B3, this standard dictates the quality of the tinned copper used in SIS conductors. It specifies the corrosion resistance as well as the conductivity.
NFPA 70 (NEC)
The NEC installation guidelines for SIS wire cover the voltage and temperature ratings, proper sizing, and target environments (i.e., switchboards and control panels).
CSA C22.2 No. 210: Appliance Wiring Material Products
CSA C22.2 No. 210 is a Canadian standard that sets the requirements for safety and performance in wire materials used in Canada, including SIS.
RoHS Compliance: Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
RoHS requirements restrict the use of materials like mercury, lead, and cadmium in electronic equipment.
Temperature Rating
In addition to the standards, SIS wire will also include a temperature rating that encapsulates the abilities of the insulation materials to withstand dry thermal environments. Most SIS is rated for 90°C (194°F).
Voltage Rating
As mentioned above, most SIS wire is rated for 600 volts. This makes the wires suitable for switchboard and control panel applications.
Get the Right SIS Wire from IEWC
Once you understand the important specifications for SIS wire—from materials used to industry standards and ratings—you can select the ideal product for your wiring setup. These guidelines help ensure the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
At IEWC, we carry a vast selection of wire products, including SIS wire. Our products meet the highest industry standards for quality, so you can rest assured you always have the best wire for the job.
If you have any questions or need assistance navigating your wire selection, please reach out to our team. We’re happy to help you find the right safety and performance for your target application.
Related Resources

What is a Wire?
Wire refers to a single, usually cylindrical, strand or rod of metal which is used to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Learn More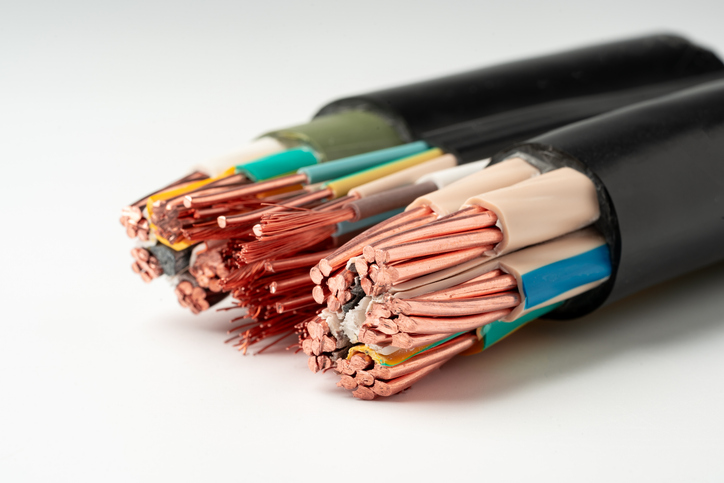
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
Selecting a Conductor
Even in the design of a simple single insulated wire many factors must be considered, including physical properties of the conductorLearn More


