Technical Guide
Take the guesswork out of wiring and cabling with IEWC’s Technical Guide, your trusted companion for all things technical. From beginner-friendly tutorials to advanced material specifications, this page is packed with resources that simplify complex projects. Dive into practical how-to guides, explore industry compliance standards, and uncover troubleshooting tips to overcome challenges with ease. Whether you’re in the electrical, automotive, or industrial sector, our comprehensive library of resources ensures that you’re always equipped with the knowledge to succeed. Make smarter, more informed decisions and ensure the highest quality in your work with IEWC’s expert-backed content.
Wire & Cable Overview
Explore essential insights into wire and cable types, applications, and specifications to ensure the perfect fit for your projects.

Stranding Classes
Strand construction in wire and cable is crucial because it directly affects flexibility, durability, and electrical performance, impacting the overall reliability and efficiency of the cable in various applications.Learn More
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Compounds
Low Smoke Zero Halogen refers to the behavior of chemical compounds when combusted - specifically the quantity of smoke generated and the toxicity of the emissions.Learn More
Basic Ampacity Values
Ampacity, or current carrying capacity, is defined as the current a conductor can carry before its temperature rise exceeds a permissible value.Learn More
Welding Cable Ampacities
Welding Cables have specific ampacity, or current carrying capacity, values.Learn More
Hook Up Wire and Lead Wire
Hook up wire and lead wire are typically single conductor wires insulated with plastic or rubber. These are the wires you most commonly see in electronic equipment—in switchboards, panels, and circuitry in a variety of household and even industrial applications.Learn More
UL 1015 Hook-Up Wire Guide
Explore the ins and outs of UL 1015 hook-up wire, gaining a deeper understanding of its uses and advantages. Read More
Cable Installation Guidelines
Care must be taken with any flexing application during the installation of the cable. Learn More
Test Procedures for Flame Retardancy
Flame Retardancy in a cable describes the ability of the materials to cease burning once the source of heat is removed. Several tests have been formulated to measure this property.Learn More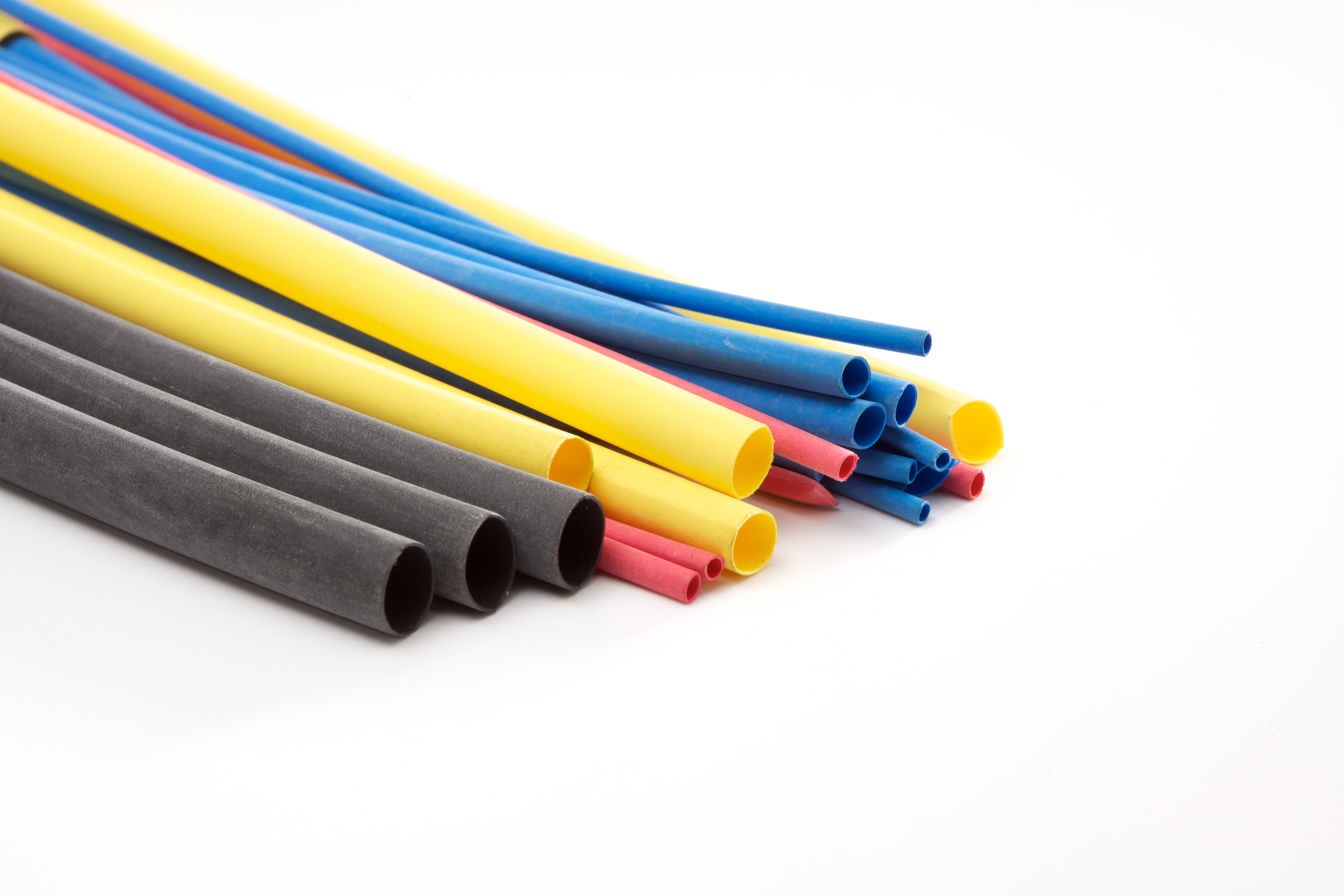
Insulation Durometer Hardness
When selecting insulation materials for a variety of applications, durometer hardness plays a crucial role in determining the material's suitability.Read More
Pulling Tensions
Pulling tension is a crucial factor when installing cables, especially in large-scale electrical systems or long cable runs.Learn More
CSA & UL Style Comparison Guide
In the world of electrical applications, choosing the right wire is essential for a seamless and efficient connection. Learn More
High Voltage Wire & Cable Guide
High-voltage or HV wire and cable are necessary for many industrial applications that rely on dependable high-power transmission.Read More
Wire Insulation Guide: Types & Applications
Insulation is a critical component of any wire conducting an electrical current . The right type of wire insulation is determined by numerous factors, including stability, required life, dielectric properties, temperature and moisture resistance, mechanical strength, and flexibility.Learn More
Twisted Component Cable Constructions
Cables composed of twisted components generally have better flexibility characteristics than parallel conductor cables.Learn More
Switchgear Cable Solutions for Safe Electrical Circuit Operations
Whether you work in power distribution or building systems, you probably know that switchgear plays a key role in keeping your electrical circuits running safely and reliably.Learn More
Wiring Distribution Panels: Effective Power Distribution Across Circuits
Distribution panels, breaker panels, load center, and/or distribution boards—any name you call them, they're a key part of every electrical system.Learn More
Transformer Wiring: Choosing the Right Cable for Voltage Management
Electrical distribution is dependent on transformers. They allow for an increase or decrease to help ensure that power moves safely and effectively through grids, industrial systems, and other operations.Learn MoreThis vs That
Compare products, materials, and solutions side-by-side to make informed decisions for your specific needs.
SJOOW vs. SOOW Cable
If you’re looking for multiconductor cords , chances are you’re trying to decide between SJOOW vs. SOOW cords. Both common conductor cables are used in electrical applications, are durable, and ideal for many projects.Learn More
Building Wire Guide - THHN vs. Other
In the world of building wire, there are several common choices available that at first appear quite similar. Learn More
Choosing Between Riser vs. Plenum Cable
Many situations require self-extinguishing and non-flammable cables, such as riser and plenum cables.Read More
Low Voltage vs. Medium Voltage Cables
Selecting the right low voltage cable or medium voltage cable is crucial for ensuring efficiency, safety, and compliance in electrical systems. The voltage rating determines the cable’s insulation, construction, and application.Learn MoreHow To
Find step-by-step guides and expert tips to help you tackle wiring, cabling, and installation projects with confidence.

How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More
Selecting a Conductor
Even in the design of a simple single insulated wire many factors must be considered, including physical properties of the conductorLearn More
Jacket Selection
The jacket or sheath physically protects the internal components of a cable, improves the cables appearance, provides flame, mechanical, thermal, chemical and environmental protection to the conductors and components.Learn More
DeReeling Procedures
In order that cables may run straight, special care should be taken not to twist the cable during handling.Learn More
VFD Cable Selection Guide
There’s nothing quite as important as motor performance in industrial automation. That’s why cable selection is crucial. The right cable choice can make or break the outcome, especially for Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs).Learn More
Choosing Turbine Control, Motor, & Instrumentation Cables
Turbine control systems and other demanding industrial environments require reliability at all times. Learn MoreWhat is?
Discover clear explanations and definitions for key concepts, materials, and technologies in the wiring and cabling industry.

What is a Wire?
Wire refers to a single, usually cylindrical, strand or rod of metal which is used to carry electricity and telecommunications signals. Learn More
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
GPT Wire
GPT wire is one of the most common types of wire in the automotive industry. If you’re looking at the wire inside a vehicle, chances are you’re looking at GPT wire. Read More
Flat Cable
Although flat jacketed cable can be constructed from the same range of wire types as those used in ribbon cable, in practice this configuration is usually restricted to vinyl insulated wires and vinyl jackets.Learn More
Tray Cable
Across industry tray cable (type TC) is a go-to solution that works in some of the harshest indoor and outdoor environments. Tray cable is a strong cable option, with many different features that make it ideally suited for an array of applications. Learn More
Shielding
Shielding refers to a sheet, screen, foil or braid used to contain electrical energy so that the signal on the cable does not radiate and interfere with signals in other nearby cables and circuitry. Shielding also protects the signal from external interference.Learn More
Armor
Armor refers to mechanical protection for cables; usually a helical winding of metal tape placed over the outer sheath.Learn More
SIS Wire
SIS wire, or Stranded Insulated Switchboard wire, is crucial in the electrical industry because of its flexibility, reliability, and adherence to strict standards.Read More
Tape Cable
Tape cable, also known as flat cable , flat conductor cable (FCC), flat flexible cable, and laminated cable, is a versatile and increasingly popular choice for electronic interconnections.Learn More
Ribbon Cable
Ribbon cables are flat multi-conductor configurations in which the individual components are easily separated.Read More
Trailer Cable
Trailer cable wires support and supply power for trailer lights and brakes—a crucial job when moving heavy equipment.Learn More
Communication Cable
Communication cable and telecom wire offer high-speed and high-performance connections for many industries.Learn MoreWire Management
Learn effective strategies, tools, and tips for organizing, protecting, and maintaining wire and cable systems.

Wire Management in Industrial Automation
This guide will delve into the essentials of wire management in industrial automation , covering types of cables, wire management tools, best practices, and the importance of organized cabling for overall system performance.Learn More
Automotive Wire Management
Whenever you’re securing wire for automotive use, it’s important to use cable management solutions such as sleeves, tubing, and ties. Read More
Cable Ties for Wire Management
Cable ties, also known as zip ties, are fastening devices designed to bundle and secure wires, cables, or other items. They come in a variety of materials, sizes, and designs, making them suitable for industrial, commercial, and residential use.Learn More
Cable Sleeving for Wire Management
Cable sleeving is the process of encasing wires in a durable and versatile protective covering. This guide explores everything you need to know about cable sleeving, from selecting the right materials to understanding its applications.Read More
Application and Selection of Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing is an essential component in wire management, offering a combination of electrical insulation, mechanical protection, and environmental sealing. This guide provides an in-depth look at heat shrink tubing, including its applications, properties, brands, and selection process.Learn MoreStandards & Specifications
Explore essential insights into wire and cable types, applications, and specifications to ensure the perfect fit for your projects.

Color Codes
Many different wire identification rely on color codes and not all color codes are the same.Learn More
Suggested Ampacities
Ampacity, or current carrying capacity, is defined as the current a conductor can carry before its temperature exceeds a permissible value. Learn More
Motor Lead Ratings
With electric motor performance and safety, the choice of insulation materials and wire temperature ratings is critical. The UL1446 motor insulation standards and IEEE test guidelines outline specific requirements to help ensure the longevity and safe operation of motors. These standards categorize insulation systems into different classes, each with a corresponding minimum wire temperature rating.Learn More
Properties of Common Thermoplastic and Thermoset Compounds
Thermoplastic and Thermoset compounds are types of polymers with different melting points and tensile strength.Learn More
Industry Organizations & Standards
Understanding industry organizations and standards is essential for anyone involved in manufacturing, installation, or regulatory compliance.Read More
Extruded Compounds and their Resistance to Industrial Chemicals
When it comes to industrial applications, selecting the right material for resistance against various chemicals is important.Read More
Chrysler & Ford Specifications Conversions
With automotive wiring systems , especially with brands like Chrysler and Ford, it is important to understand the wire specifications.Read More
High-Temperature Cable Tie Types & Ratings
While cable ties may seem like a minor consideration, they do an outsized job. In high-temperature applications and corrosive environments, a cable tie binds and bundles cables together, keeping spaces organized, safe, and in proper working order.Read More
Registered Trademarks
Trademarks are crucial in distinguishing products and services in the wire and cable industry. Read More
Security & Fire Alarm Cable Standards
What comes to mind when you think of fire and security systems? Probably smoke detectors and alarms blaring, cameras recording, and doors locking into place. What's less visible, but essential to the scenario, is the fire and security system cabling that connects and powers it all throughout the building.Read MoreCharts
Access comprehensive charts and reference tables to simplify your wire and cable selection and planning process.
UL, Metric & SAE Strand Charts
Discover additional information on UL, Metric and SAE Strand ChartsLearn More
Electronic Current Ratings
As an electrical current flows through a conductor, heat is generated. Since heat must be dispersed, many factors must be considered before a safe current rating can be used in a wire and cable construction. Learn More
Metric Conversion Table
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered including size and conversions. Learn More
Application & Selection Guide for Standard Product
Read more on the typical applications for standard wire and cable products.Read More
Wire Ampacity Chart & Guide
Are you looking for the best wire size for your application? A wire ampacity chart is a critical tool that can help you make the determination. Read More
Temperature Conversion Table
Temperature conversion is crucial for the performance and safety of cables and wiring.Learn More
Portable Cord Guide
Portable cord, also referred to as flexible cord, extension cord or portable cordage, is a multi-conductor cable used for temporary electrical connections.Learn MorePopular Types
Explore the most commonly used wire and cable types, their features, and ideal applications for your projects.

Types of Strand Construction
Strand construction in wire and cable is crucial because it directly affects flexibility, durability, and electrical performance, impacting the overall reliability and efficiency of the cable in various applications.Learn More
Popular Jacket Types
Jackets cover and protect the enclosed wire or core against damage, chemical attack, fire and other harmful elements which may be present in the operating environment. Learn More
Popular Insulation Types
Insulation is a critical component of any wire conducting an electrical current . The right type of wire insulation is determined by numerous factors, including stability, required life, dielectric properties, temperature and moisture resistance, mechanical strength, and flexibility.Learn More
Tape Types
Plastic tapes are rarely used as a primary insulation in electronic wires because such wires, as compared with those having extruded insulations, are relatively expensive.Learn More
Popular Shielding Types
In situations with long signal runs or complex circuits, shielding becomes a crucial part of reducing interference and maintaining signal integrity. Learn More
Popular Armor Types
When it comes to protecting cables, choosing the right armor type is crucial. Learn MoreIndustries
Discover tailored wire and cable solutions designed to meet the unique demands of various industries and applications.

Automotive Battery Cable Specifications
Some common questions arise regarding automotive battery cable specifications and the usage of cables in other applications.Read More
Automotive Primary Wire
Automotive primary wire is a type of electrical wire that is used in automotive applications. Read More
Automotive Industry Wiring Standards
The automotive industry has long relied on a set of standards to ensure the safety and reliability of vehicles.Read More
Electric Vehicle Wiring Specifications
As consumer demand continues to rise, so does the need for electric vehicle wire, cable, and other charging components.Learn More
Data Center Connectivity & Networking Solutions
Data centers are all about connectivity. When you’re transmitting high-speed data and information across cable and wire, you need the best in terms of performance and reliability. Network devices and tools play a crucial role in data center operations. Learn More
Expert Guide to Industrial Automation Cables
Since the early days of manufacturing, automation has played a crucial role. As technology forges ahead, so does the need for reliable industrial automation cables to connect and network components for data exchange.Read More
Military & Government Wire Specifications
When it comes to military and government applications, wiring and cabling meet the highest standards of durability, reliability, and safety. Learn More
SIS Wire Specifications
SIS (Switchboard Instrumentation and Switchgear) wire is a versatile wire used for many different electrical and switchboard cable applications.Read More
Power Distribution System Design for Industrial Environments
Industrial environments require power. A reliable power distribution system ensures that the heavy machinery, lighting, and control systems work without interruption. Electrical systems require special planning and diligence. Learn More
Selecting Wire and Cable Solutions for HVAC
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems require reliable, durable, energy-efficient wiring solutions for smooth operation, safety, and compliance with industry regulations.Learn More


