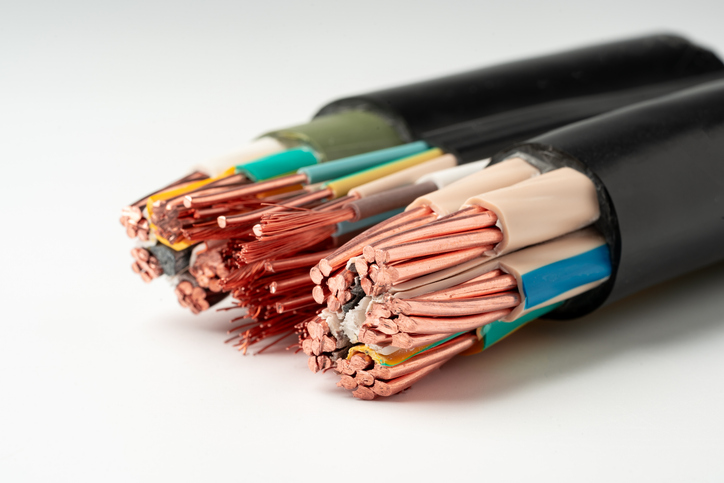
Shielding
 Shielding is a vital aspect of cable design, providing a protective barrier that confines electrical energy within the cable. This shielding prevents signal leakage, which could lead to interference with nearby cables or sensitive electronics. It also safeguards the cable's signal from external sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring the data remains intact and reliable.
Shielding is a vital aspect of cable design, providing a protective barrier that confines electrical energy within the cable. This shielding prevents signal leakage, which could lead to interference with nearby cables or sensitive electronics. It also safeguards the cable's signal from external sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring the data remains intact and reliable.
Types of Cable Shielding
Understanding the different types of shielding can help you choose the right one for your application. Here are the most common types:
1. Braid Shielding
Braid shielding consists of woven metal strands, typically made from copper or aluminum. It is known for its flexibility and durability, making it suitable for applications that require frequent movement or bending. While it offers excellent mechanical strength, it provides moderate shielding effectiveness.
2. Foil Shielding
Foil shielding, usually composed of aluminum or Mylar-aluminum laminate, is a lightweight and thin option. It offers near-complete coverage, making it highly effective against high-frequency interference. However, foil shielding is less durable and more susceptible to damage during installation or in high-flex environments.
3. Spiral (Serve) Shielding
Spiral shielding involves metal wires wrapped around the cable in a spiral pattern. This type of shielding is highly flexible, ideal for cables that need to bend or flex frequently. Despite its flexibility, spiral shielding provides less consistent coverage compared to braid or foil shielding, especially at higher frequencies.
Key Factors in Shielding Selection
Choosing the right shielding involves evaluating several factors to ensure optimal performance:
Shield Effectiveness
The primary goal is to provide adequate protection against EMI. Effectiveness depends on the coverage, material, and construction of the shield. Foil shielding is often preferred for high-frequency applications due to its complete coverage, while braid shielding is better suited for low-frequency applications.
Flexibility
In applications requiring frequent bending or movement, such as robotics or mobile equipment, flexibility is crucial. Braid and spiral shields generally offer greater flexibility than foil shields.
Flex Life
Flex life refers to the cable's ability to endure repeated bending without performance degradation. Spiral and braid shields usually offer a longer flex life compared to foil shields.
Ease of Stripping and Terminating
Different shielding types vary in ease of stripping and terminating, affecting installation and maintenance. Braid shields may require more effort to prepare, while foil shields are often simpler to handle.
Mechanical Strength
Shielding should provide adequate mechanical protection to withstand physical stresses. Braid shielding excels in this area, offering robust protection in demanding environments.
Resistance to Corrosion
For cables exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive elements, the shield material must resist degradation. Copper and tinned copper braids offer good corrosion resistance, while aluminum foil shields might need additional coatings for enhanced durability.
Cost
Budget considerations also play a role. Braid shielding is generally more expensive due to the material and manufacturing process, whereas foil shields offer a more cost-effective solution, particularly in applications where flexibility is less critical.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers and designers can select the most suitable shielding type to ensure reliable, interference-free signal transmission. Contact IEWC to talk to a dedicated team member and learn more about how we can be your complete partner!
Related Resources

How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More
Popular Shielding Types
In situations with long signal runs or complex circuits, shielding becomes a crucial part of reducing interference and maintaining signal integrity. Learn More
Armor
Armor refers to mechanical protection for cables; usually a helical winding of metal tape placed over the outer sheath.Learn More