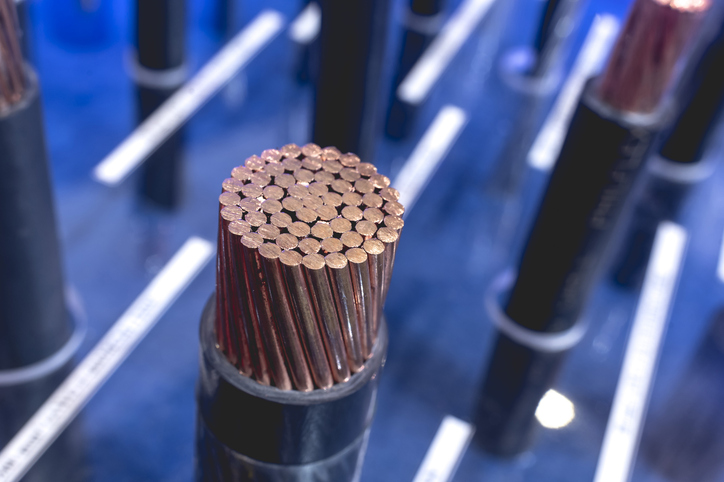
Switchgear Cable Solutions for Safe Electrical Circuit Operations
Switchgear Cable Solutions for Safe Electrical Circuit Operations
Whether you work in power distribution or building systems, you probably know that switchgear plays a key role in keeping your electrical circuits running safely and reliably.
Much of the switchgear system relies on cables to connect and distribute power. Today, we’ll explore those types of switchgear cable solutions, their properties, resistance ratings, and compliance with safety standards.
Need more help with your switchgear cable selection? Reach out! We’re happy to help you decide on the best solution for your application.
your application.
Key Cable Types for Switchgear Applications
Within most switchgear systems, there are an array of cables. Cable types perform different tasks for different applications. Here are the common cable solutions found in switchgear.
1. Power Cables
Power cables carry high-voltage electricity to and from switchgear systems. They ensure that the building, area, or application powered by the switchgear system is safely and consistently distributed. The cables typically consist of wire conductors insulated with a temperature-resistant material. Switchgear power cables connect power sources, busbars, and loads.
Most power cables contain copper conductors due to copper’s high electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. However, aluminum conductors are also common and offer cost and weight savings—particularly for larger cables. Aluminum is less flexible and features lower conductivity compared to the copper options.
The temperature-resistant insulation further protects these cables to prevent electrical leakage and safety hazards. The popular insulation materials in power cables are XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), EPR (ethylene propylene rubber), and PVC (polyvinyl chloride). XLPE offers high-temperature resistance and excellent insulation. EPR is flexible and resistant to chemicals as well as heat. PVC is a standard, cost-effective insulation for low and medium-voltage power cables.
Shielding protects the power cables from electromagnetic interference, or EMI, and helps add another layer of safety for high-voltage applications. Typically, shielding is made of copper tape or wire for grounding and EMI. Sometimes, semi-conducting tape or layers help to control electric stress.
Optional armoring protects power cables in particularly harsh environments and areas of mechanical stress. The armoring is often steel or aluminum (used in single-core cables). The outer sheath of the power cable gives yet another layer of protection. The sheath is often PVC but may also be LSZH (low-smoke zero halogen) for increased fire safety or PE (polyethylene) for UV and moisture resistance in outdoor environments.
Power Cable Features:
- High voltage ratings for safe power transmission and use in distribution systems.
- Robust insulation to prevent electrical hazards and damage.
- Typically made from copper or aluminum conductors surrounded with PVC, XLPE, or EPR insulation. Shielding is used to protect from EMI.
Power cables are commonly used in substations and for industrial power systems. They are used within the switchgear for renewable energy grids as well. They come in a wide range of options to ensure you have the ideal temperature and safety standard for your project.
2. Control Cables
How do you control signals within switchgear? Control cables carry those signals needed for monitoring and operational management. Control cables have robust insulation for extra safety.
Control cables inside switchgear are typically made of materials designed to provide high reliability, durability, and electrical safety. The conductors inside the control cables are often copper and occasionally aluminum. Copper, again, is the preferred material with superior electrical conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion and wear. Aluminum is the lighter and less expensive choice but has lower conductivity and flexibility.
The insulation surrounding the conductive wire protects from short circuits and electrical leakage. The most common materials for control cable insulation are PVC, XLPE, and EPR (ethylene propylene rubber). PVC is inexpensive and has good insulating properties. XLPE is often used in higher temperature and voltage applications. EPR has a high resistance to chemicals as well as heat.
Control cables sometimes feature shielding to prevent EMI and protect sensitive electrical circuits. The shielding is typically made from copper tape, aluminum, or braided copper.
The outer sheath or jacket of the control cable gives mechanical protection and resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture. The outer sheath is often made from PVC, PE, or LSZH.
Depending on the application and type of control cable, they may feature single or multiple cores. Each core is insulated and color-coded to be quickly and easily identified.
Control Cable Features:
- Flame-retardant insulation for safety and protection.
- Used to interconnect relays, switches, and instruments in switchgear.
- Typically lower voltage (300-1100V); used for monitoring and signaling.
- Flexible for easy routing in small spaces.
Control cable is used in automation systems, electrical panels, and industrial controls for signaling and monitoring applications.
3. Instrument Cables
The other typical switchgear cable is instrument cable. It transmits data signals from sensors and instruments to the control center. Because of their essential purpose, they must be interference-resistant and reliable.
The conductors in instrument cables are often made from copper—either tinned or bare. Tinned copper provides better corrosion resistance in harsh environments and extreme conditions. Instrument cable is usually multi-stranded for greater flexibility.
Instrument cables are well-insulated for accurate signal transmission and to prevent electrical leakage. The insulation materials include PVC, XLPE, and PE. PVC is the most common and cost-effective choice, with XLPE being the go-to for high-temperature applications. PE is used for improving signal integrity. EPR is also used occasionally, particularly for chemical resistance.
The shielding of the instrument cables protects them from EMI and crosstalk. Aluminum foil shielding is an excellent option for 100% protection from EMI. Braided copper shielding is also protective from EMI and adds mechanical strength. A combination of foil and braid shielding may be used in noisy environments.
Instrument cables are often twisted together in pairs or triads to give a more balanced signal transmission. Pairing and twisting cables reduces the instance of EMI and helps to ensure signal integrity.
The outer sheath of most instrument cables protects them from heat, moisture, and chemicals. The sheath materials include the standard PVC, LSZH to minimize smoke and fumes in fire-sensitive environments, and PE for outdoor use.
Instrument Cable Features:
- Highly accurate cables that minimize signal loss.
- Insulated options for various environmental conditions.
- Twisted pairs and multi-core designs help prevent crosstalk.
Instrument cables are most prevalently used in power monitoring, fault detection, and circuit diagnostics due to the particularly sensitive nature of these tasks.
Essential Properties of Switchgear Cables
All switchgear cables share some essential properties. For example, all cables in switchgear must meet insulation and fire safety standards, including UL, IEEE, and IEC certifications. PVC is the most common insulation material, while XLPE is the go-to for high-performance applications that require temperature resistance.
Switchgear cables must withstand high operating temperatures, stress, and abrasion within switchgear environments. Many cables also need protective sheathing to resist oils, chemicals, and moisture.
Cables are rated to handle specific voltage amounts. Ensuring that the voltage and current ratings match the application's requirements is essential to prevent overloads and other hazards.
Benefits of Using High-Quality Switchgear Cables
When choosing switchgear cables, it may seem logical to opt for the most widely available cable and/or the least costly. While the cost differential can be fairly nominal, it’s important to invest in the highest quality switchgear cables. Why? Here are several reasons why you should prioritize quality when it comes to cables:
- Improved Safety: The right cable insulation and resistance help reduce the risks of electrical faults, overloads, and fire hazards.
- Reliable Performance: High-quality cabling materials help you make sure that power delivery is consistent and signal integrity is strong.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Regulatory and operational requirements are there to protect your team and your equipment.
IEWC offers a wide range of the highest quality cables and wiring for switchgear applications. Our comprehensive inventory includes power and control cables, specialized instrument cables, and all other switchgear requirements.
Are you looking for custom solutions? We can help you find the best product to meet all your operational requirements. At IEWC, our products provide the long-term stability and durability needed for your most important applications. Reach out today for cable and wiring that offers consistently reliable power distribution and safety.
Related Resources
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More
Selecting a Conductor
Even in the design of a simple single insulated wire many factors must be considered, including physical properties of the conductorLearn More


