VFD Cable Selection: Reducing Interference in Motor Drive Systems
There’s nothing quite as important as motor performance in industrial automation. That’s why cable selection is crucial. The right cable choice can make or break the outcome, especially for Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs).
Here’s how to select the wiring and cable you need for optimal VFD power transmission.
The Importance of VFD Cables
VFDs are used across many industries to control an electric motor's speed and torque. Just as the name implies, these VFDs vary in the frequency and power voltage supplied to the motor. VFDs allow for precise adjustments and energy-efficient automation in industrial applications.
How does a VFD work? It uses a rectifier to convert the standard AC power supply (usually between 50-60 Hz) into DC power. Then, using an inverter, the VFD converts the DC power back into AC at a controllable frequency and voltage. VFDs are used to adjust the motor speed with lower frequencies yielding a slower spin, and higher frequencies resulting in faster motors.
There are several advantages to VFDs, many of them cost-related. Better process control improves operational efficiency. Soft-starting motors and cutting back on mechanical stress extend overall equipment life and prevent wear and tear. VFDs also allow you to adjust power to meet demand—helping cut energy consumption and related costs.
Which industries rely on VFDs? They’re used throughout industrial automation in conveyors, pumps, and robotic arms to assist manufacturing and processing. VFDs are also used in HVAC and water treatment pumps, compressions, and aeration systems.
VFDs generate high-frequency electrical noise, so it’s crucial that you select the proper VFD cables to minimize interference and protect your systems.
VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) cables are specialized power cables specifically designed for their main job: connecting VFDs to electric motors. These cables are engineered to handle instances of high-frequency voltage spikes, EMI (electromagnetic interference), and harmonic distortion much better than standard power cables.
EMI is quite common in motor drive systems and can greatly impact system performance, efficiency, and longevity. VFD cable helps you maintain reliable motor control, cutting back on downtime and ensuring that equipment complies with important industry standards.
Considerations for VFD Cables in Motor Drive Systems
A VFD cable is a specialized power cable that connects drive systems and motors, transferring electrical signals and helping manage the power flow. The cables protect against electrical noise and ensure smooth operation of your equipment.
There are many important considerations when you choose a VFD cable.
Cable Shielding
Shielding is key to preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reducing noise in VFD applications. There are many different types to choose from: foil shields, braid shields, and combinations.
- Foil Shields: Best for high-frequency EMI, these shields consist of a thin layer of aluminum foil wrapped around the cable conductors and often paired with a drain wire for grounding. These are ideally suited for controlled environments with less physical stress, as they can be prone to breakage if moved and flexed.
- Braid Shields: Best for low-frequency EMI and mechanical durability, braid shields are made up of a thicker woven mesh of either copper or tinned copper wires surrounding the conductors. These offer electrical shielding along with physical strength for high-vibration and high-movement environments.
- Combination Shields: Combination shields can be a good choice to get the best of both worlds—high and low-frequency shielding. These shields are best suited for environments with higher EMI exposure and sensitive electronic applications. They are more expensive than foil shields but can offer significant advantages for the right application.
Voltage Rating
Like many types of cable, voltage levels apply. Because VFD cables operate with high electrical stress due to EMI and fluctuations, it's crucial that you choose the correct voltage rating and insulation type for your application.
VFD cables can handle a range of different voltage levels—from 600V to 2000V (and beyond in some cases). It's important to look at the motor's operating voltage when deciding. As a general guideline, select a VFD cable rated at least 25% above the motor's operating voltage to ensure it can withstand any voltage spikes.
- Low-Voltage VFD Systems (≤600V): Commonly in smaller motors, conveyors, and HVAC systems
- Medium-Voltage VFD Systems (600V – 2000V): Many industrial automation applications fall into the medium voltage range, such as manufacturing and pumping systems.
- High-Voltage VFD Systems (2000V+): This voltage level is found in the heaviest-duty applications—mining, oil, gas, and large-scale manufacturing.
Insulation Type
Insulation provides critical protection for wires amid high electrical stress, harsh environments, and temperature fluctuations. That means the insulation material must offer dielectric strength along with thermal resistance.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Best for light-duty VFD allocations (≤600V). PVC insulation is typically an affordable, flexible solution that offers some oil and chemical resistance but lower heat resistance.
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Ideally suited for medium to high voltage VFDs (600V-2000V). XLPE offers strength and heat resistance while reducing electrical noise. It's typically the most widely used insulation for VFD cables.
- EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber): EPR is a good choice for the most extreme environments and high-flex applications. It offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance.
Cable Conductor Materials
Material matters greatly when it comes to the cable conductor. The conductor material will directly impact the cable's performance, flexibility, and cost. There are two options: copper vs. aluminum.
- Copper: Flexible and durable, copper is a great choice for high-conductivity applications. Copper is resistant to corrosion and has excellent power transmission. It can be heavier and more expensive, so choosing the right conductor for your particular needs is important.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is the cost-effective, lighter-weight choice. It allows for easy insulation. Aluminum is more prone to oxidation, so it needs anti-corrosion treatment. It also has lower conductivity, so you will need a higher gauge to carry the same current.
As a general rule, copper is the preferred choice for VFD cables. Aluminum is a good choice for cost- and weight-sensitive large-scale applications but requires a higher gauge.
Wire Gauge Size Considerations
The wire gauge size is another important consideration for VFD cable selection. This is crucial for minimizing voltage drop over long distances, reducing overheating and power loss, and ensuring efficient motor performance.
You'll want to examine your motor power and current load to select the right gauge. Larger motors will require thicker cables to handle the higher current. Gauge also factors in when considering the distance between the drive and motor. The longer the cable needs to run, the larger the wire gauge is needed to prevent voltage drop.
- ≤50 feet (short runs): Standard gauge for motor rating.
- 50-150 feet (medium runs): 1-2 sizes larger than standard.
- 150+ feet (long runs): Up to 2-3 sizes larger to minimize voltage drop.
When selecting a wire gauge, it’s often better to go bigger. A larger gauge (in other words, one with a lower AWG number) will offer better power delivery and reliability.
Choosing the Right VFD Cable for the Application
If you’re ready to select the ideal VFD cable for your particular application, it’s important to look at all the factors: motor drive requirements, operating conditions, and any environmental hazards.
Match the cable specifications to the motor drive requirements. The cable should be able to handle the peak voltage of your drive system. For VFD applications, that means 600V, 1KV, or even 2kV cables to stand up to voltage spikes.
Conductor size is also important. Choosing the right gauge is essential to ensure minimal voltage drop and power loss. Your size selection will often be based on the motor current ratings as well as the needed cable length. VFD cables will feature shielding—copper braid, aluminum foil, or composite to block EMI.
Environment plays a big factor in your decision. You’ll need to select cables rated for an appropriate temperature setting. For heat exposure, XLPE-insulated VFD cables are often the best choice. In environments with chemical and oil exposure (e.g. oil, gas, food processing, automotive manufacturing) the cables will need to have PVC or TPE jackets for protection. UV exposure should also be considered for cables in outdoor environments.
VFD Cables should meet your flexibility and bend radius needs. Cables are often installed in tight spaces or in dynamic applications where flexibility and movement is important. Your VFD cables should help mitigate harmonic distortion and protect from EMI and system interference.
If you need assistance selecting the proper VFD cable to minimize interference and ensure reliable motor drive system performance, reach out to IEWC. Our cable and wire experts can help you find the best cable to maximize the safety and efficiency of your industrial automation applications.
Related Resources
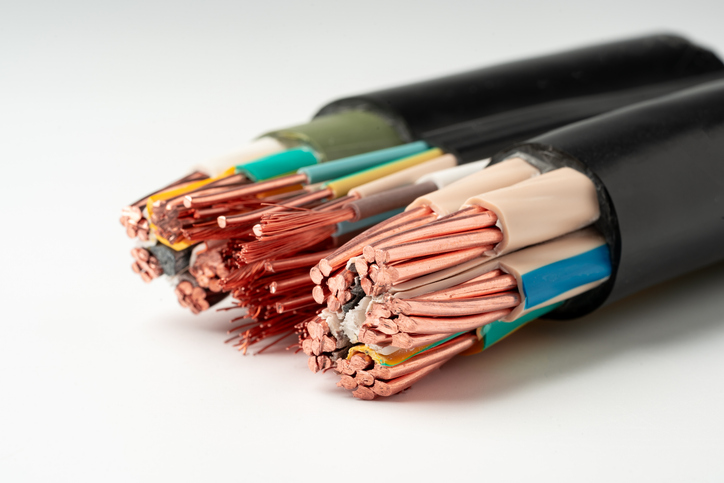
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
High Voltage Wire & Cable Guide
High-voltage or HV wire and cable are necessary for many industrial applications that rely on dependable high-power transmission. Whether you’re looking for the right HV cable for your application or trying to learn more about how HV wire and cable work, we’ll break it down for you.Learn More
How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More


