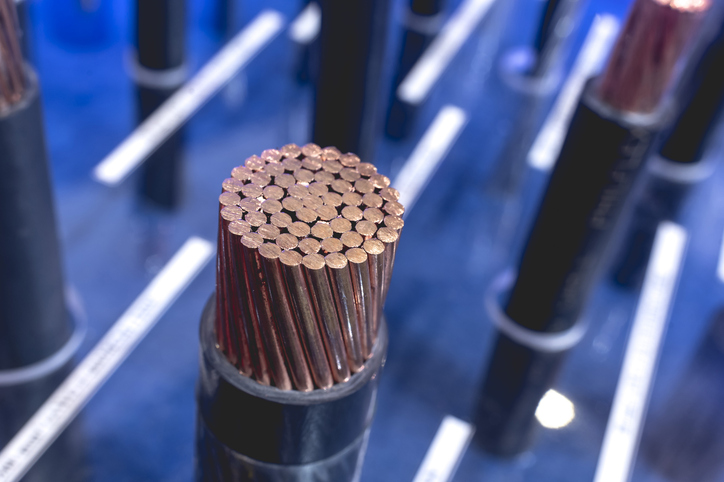
What is a Wire?
A Comprehensive Guide to Wire
 Wire is a fundamental component in the transmission of electricity and telecommunications signals. Typically, wire consists of a single, cylindrical strand or rod of metal, formed by drawing metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. In a broader sense, "wire" can also describe a bundle of such strands, known as "multi-stranded wire." In mechanical contexts, this is referred to as wire rope, while in electrical settings, it is called a cable.
Wire is a fundamental component in the transmission of electricity and telecommunications signals. Typically, wire consists of a single, cylindrical strand or rod of metal, formed by drawing metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. In a broader sense, "wire" can also describe a bundle of such strands, known as "multi-stranded wire." In mechanical contexts, this is referred to as wire rope, while in electrical settings, it is called a cable.
Types of Wire Cross-Sections
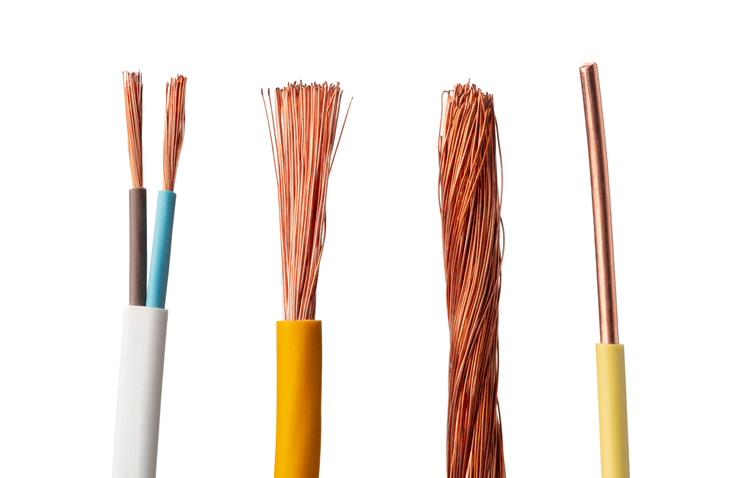
Although wire is usually circular in cross-section, it can be manufactured in various shapes such as square, hexagonal, and flattened rectangular. These different cross-sections serve both decorative purposes and technical applications, such as in high-efficiency voice coils used in loudspeakers.
Understanding the Manufacturing Process
Wire manufacturing involves drawing metal through a die, ensuring the wire achieves the desired thickness and strength. Common materials used include copper, aluminum, and specialized metals like tungsten or titanium. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Materials Commonly Used in Wire Manufacturing
- Copper: Highly conductive, commonly used in electrical wiring.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective, used in power transmission lines.
- Steel: High tensile strength, used in wire ropes and heavy-duty applications.
Applications in Various Industries
Wire's versatility makes it indispensable in many industries, some examples include:
- Industrial Automation: Wires are crucial for the broad range of equipment used to automate manufacturing processes, machinery and other equipment.
- Power Distribution: The power distribution market involves a wide range of equipment required for efficient power transmission and management.
- Specialty Electric & Hybrid Vehicles: Choosing the perfect wire and cable for your specialty electric vehicles is critical in ensuring optimal performance under challenging conditions.
- Automotive: Automotive electrical wire is a type of wire that is specifically designed to be used in the electrical systems of vehicles.
For more industries and detailed applications, visit our Industry page.
Benefits of Multi-Stranded Wire
Multi-stranded wire, often called wire rope or cable, offers flexibility and strength, making it ideal for dynamic applications. Its use is prevalent in mechanical systems requiring robust and reliable components. For more information, see our Wire Stranding Classes and Type of Strand Construction technical guides.
Innovations in Wire Technology
Wire technology is continually evolving, with new materials and manufacturing techniques enhancing performance and durability. Innovations such as superconducting wires, which offer zero electrical resistance, are paving the way for more efficient energy transmission.
IEWC can provide guidance for new product development, existing product/program re-engineering and redesign for your innovative wire needs, learn more about IEWC's Engineered Solutions.
Understanding the complexities of wire—from its various types and manufacturing processes to its wide-ranging applications—enables us to leverage its full potential across different industries. As technology advances, wire continues to be a vital component, ensuring the functionality and efficiency of countless systems and devices.
Related Resources
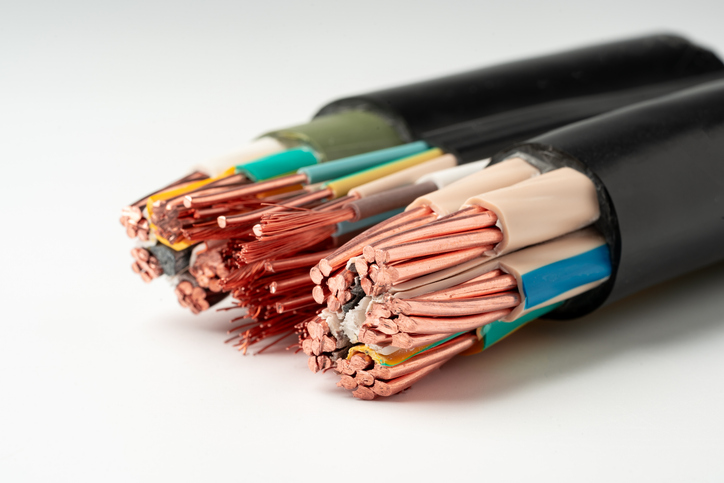
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More
Selecting a Conductor
Even in the design of a simple single insulated wire many factors must be considered, including physical properties of the conductorLearn More


