A Guide To Communication Cable
Communication cable and telecom wire offer high-speed and high-performance connections for many industries. Data transmission relies on telecom cable, and at IEWC, we carry a wide supply of cables and wire options to support businesses.
If you're considering what types of communication cables your application will require, or if you're working on new installations, we have the wire and cable you need. We'll break it down for you here in our guide to communication cable.
 Common Applications of Communication Cable
Common Applications of Communication Cable
Telecom cable can be found in many applications, including the most popular one—Ethernet cable. It's also used in other forms of data transmission, electronic circuits, and computer networking. Fiber optic cables are used throughout telecommunication as well.
Most people are familiar with coaxial cables that connect to their television. CCTV cables are frequently used in security camera applications.
Businesses rely on high-speed data transmission, and telecommunications cables transmit that data lightning fast. Telephone and network cables connect all the communication and data devices businesses depend on for service.
Some places where you may discover communication cables include fire alarms, security systems, and sound systems. Telecom cables are used throughout industrial data communication systems and business computer systems.
Types of Communication Cables
There are many different types of communication cables, but the most common are fiber optic, ethernet, and coaxial. Of course, telephone cable is also still commonplace.
The technical features of the different communication cables vary by type and factors such as voltage, shield materials, the number of twisted pairs inside the cable, and other features. Tolerance to higher temperatures and fire resistance are also considerations. Some types of communication cables are suited for outdoor and underground use, while others are more delicate.
These are the go-to cables and wires for business data and communication today.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables work with light pulses, transporting communication signals via optical fiber inside an insulated jacket. Fiber optic cable types are indicated by color and jacket codes. Indoor fiber optic cables are referred to as tight buffer types. These cables are small and flexible. The jacket or sheathing covering the cable is color-coded and marked for easy identification.
- Light Blue (Aqua): Indicates multimode cable.
- Orange: Indicates all other multimode cables.
- Yellow: Indicates a single-mode cable.
Each fiber optic cable is marked with the jacket material type. These types include Polyethylene (PE), Polyurethane (PUR), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and other non-conductive and heat-resistant coatings. The cable will also have a code specifying each cable's fire resistance and purpose. These codes include CM for general communications, not fire resistant; CMR for communications riser, for some fire-resistance between floors and inside ducts; and CMP for communications plenum, for fire-resistance in plenum (contained pressure) areas.
Ethernet and Networking Cables
Ethernet cables are the most common type of cables in many businesses and applications. Ethernet cables are twisted pair cable that comes in different categories, indicated by "Cat #" on the cable. You're unlikely to need Cat 1-Cat 5 cables in today's market. Should you require a less-common older type of ethernet cable, contact us, and we can help you troubleshoot your options.
Most ethernet cables today are Cat 5e or “enhanced” cables. These cables are twisted pair copper cables. Cat 5e cables work on up to 100MHz. The Cat 5e has tighter crosstalk specifications, eliminating signal transfers compared to lower Cat cables.
Cat 6 cables are twisted pair copper cables. These cables are used for GB Ethernet applications. They are backward compatible with lower Cat cables. Cat 6a and 6e, augmented cables are also designed for GB Ethernet applications with a maximum bandwidth of up to 500 MHz.
Cat 7 cables are always shielded. These are twisted pair cables that carry 10 GB Ethernet over 100m. However, Cat 7 isn't a recognized standard by TIA/EIA, and most users opt for Cat 6a instead. Cat 8 cable is also on the market, with a frequency of 2000MHz and speeds that can hit 40 Gbps and 30 meters.
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial or “coax cables" have been around since the late 1800s. These cables consist of an inner conductor and an insulating layer protected with an outer shield. For years, coax cables were the go-to option for AV networks, cable TV (hence the term "cable"), and radio.
Coax cables are split into RG types based on diameter and properties. Coax cable may include a single, dual, or quad shielding, which describes the type of shielding layer—a cloth-like weave (single), a metal foil around a weave (dual), or double layers of both materials.
Like other cables, markings on the outside of coax cables indicate the sleeve type. Some examples include Polyethylene (PE), Solid Teflon (ST), and Foam Polystyrene (FS). Specialty and composite coax cables are also available.
Telephone Cable
Although they aren’t as popular as they once were, telephone cables are still available and frequently used in business applications. These cables carry telephone signals (voice and sound) and are available as indoor telephone cable, outdoor telephone lines, and modular options.
Ribbon Cable
Ribbon cables are instantly recognizable to anyone who's peeked inside a computer. Ribbon cable is also known as multi-wire planar cable. Its flat surface features several small, parallel wires across the wide, flat horizontal cabling. Ribbon cable is available in round-to-flat, round conductor flat, and twisted pair flat options.
Electronic Cable
Electronic cable covers the other types of cable technology available. These cables include multi-conductor and composite cables, as well as multi-pair and triad. Electronic cables are categorized and differentiated by the gauge size, number of conductors, jacket material, and other features.
Find Communication Cable at IEWC
At IEWC, we carry many specialist cables and wire types for all your data and A/V needs. We have cable and cable accessories to help you with a wide range of data transmission and other requirements. Explore our communication cable categories to find the right option for your particular application and specs.
Reach out to us with any questions or to request a quote. As cable and wiring experts, we're here to ensure you have the right choice for safe, efficient, and dependable results.
Related Resources
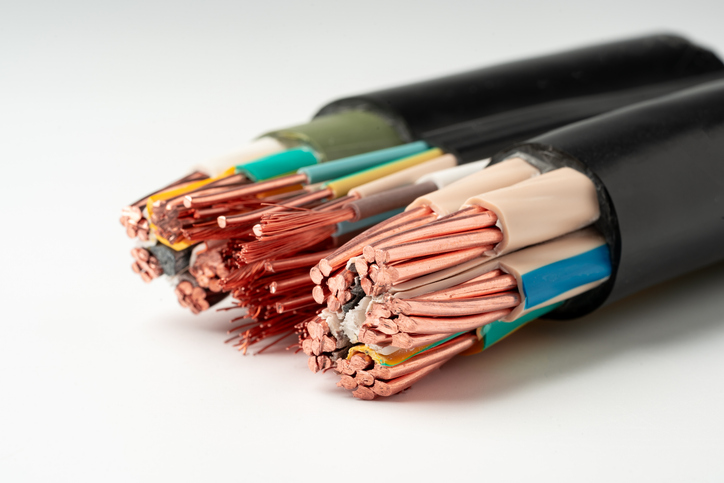
What is a Cable?
Cable, or cabling, consists of the twisting together of two or more insulated conductors.Learn More
High Voltage Wire & Cable Guide
High-voltage or HV wire and cable are necessary for many industrial applications that rely on dependable high-power transmission. Whether you’re looking for the right HV cable for your application or trying to learn more about how HV wire and cable work, we’ll break it down for you.Learn More
How to Choose the Right Wire or Cable
In selecting a wire or cable for an application, several factors should be considered. Learn More


