Application and Selection of Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing is an essential component in wire management, offering a combination of electrical insulation, mechanical protection, and environmental sealing. This guide provides an in-depth look at heat shrink tubing, including its applications, properties, brands, and selection process.
Properties of Heat Shrink Tubing
The table below highlights key properties of heat shrink tubing, including material composition, shrink ratio, and temperature resistance, helping users choose the right option for their specific application.
|
Property
|
Description
|
Common Values
|
|---|---|---|
| Material | The composition of the tubing affects flexibility, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals. | Polyolefin, PVC, Teflon |
| Shrink Ratio | The ratio indicating how much the tubing shrinks in diameter when heated, ensuring a snug fit. | 2:1 (shrinks to half its size) |
| Shrink Temperature | The temperature at which the tubing begins to contract, allowing it to conform tightly around components. | ~90°C |
| Operating Temperature | The range of temperatures in which the tubing can function effectively without degradation. | -55°C to 135°C |
Applications of Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing is widely used across industries due to its versatile properties. Some of its primary applications include:
- Electrical Insulation: Covers exposed wires and connectors, preventing short circuits and enhancing safety by providing a non-conductive barrier.
- Strain Relief: Reduces mechanical stress on electrical connections, protecting them from bending or pulling forces that could lead to failure.
- Environmental Protection: Shields from external elements such as moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor and harsh environments.
- Wire Bundling: Organizes multiple wires into a single, manageable group, reducing clutter and improving overall cable management.
- Identification: Utilized for labeling and color-coding wires, which simplifies circuit management and troubleshooting tasks.

Brands that Meet Diverse Requirements
IEWC provides a diverse selection of heat shrink tubing from industry-leading brands known for their quality and performance. Each brand specializes in different aspects of heat shrink tubing, catering to a range of applications:
- Dunbar: Specializes in general-purpose and industrial-grade heat shrink tubing, offering a balance of flexibility and durability for common electrical applications.
- Sumitomo: Known for high-performance tubing with superior electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and long-term durability, often used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Alpha Wire: Focuses on extreme-environment applications, offering rugged, high-temperature-resistant tubing ideal for harsh industrial and military conditions.
- Qualtek: Supplies a wide selection of cost-effective heat shrink tubing solutions, including thin-wall, dual-wall, and specialty options designed for electronics, automotive, and industrial applications.
- HellermannTyton: Features innovative heat shrink solutions with strong adhesive properties, ensuring a reliable seal in moisture-prone environments such as marine and underground applications. Their tubing is widely used in critical electrical insulation applications.
- TechFlex: Specializes in braided sleeving and high-performance heat shrink tubing for applications requiring superior abrasion resistance and flexibility. Often used in aerospace, military, and industrial applications where extreme durability is required.
- DSG-Canusa: Provides advanced heat shrink tubing solutions, including adhesive-lined and dual-wall options, ensuring strong environmental sealing and protection against harsh conditions.
Each of these brands provides unique advantages, ensuring that customers can find the right tubing solution for their specific needs. If you have questions about the capacity of any wire management product, contact IEWC.
Selecting the Right Heat Shrink Tubing
Selecting the right heat shrink tubing involves understanding the requirements of your application. Here are the key steps to making an informed decision:
- Determine Application Requirements: Identify whether insulation, protection, bundling, or identification is the main purpose. There are a variety of material options, here are the most commonly used:
- Polyolefin: Most widely used, offering flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals and heat.
- PVC: More cost-effective with good insulation properties but less heat resistance.
- Fluoropolymer (PTFE, FEP): High-performance tubing with superior chemical and temperature resistance.
- Measure Components: Ensure the tubing’s expanded diameter accommodates the component while achieving a snug fit after shrinking.
- Select the Appropriate Shrink Ratio: Choose a ratio that provides the necessary compression.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Account for exposure to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations.
- Review Regulatory Standards: Ensure compliance with industry-specific safety and performance requirements.

Find Heat Shrink Tubing at IEWC
Heat shrink tubing is a critical tool in wire management, providing insulation, protection, and organization for electrical systems. By understanding its properties, selecting the right type for the application, and following proper installation techniques, users can enhance the durability and safety of their electrical connections.
Explore IEWC’s extensive range of heat shrink tubing today and find the perfect fit for your needs.
Related Resources
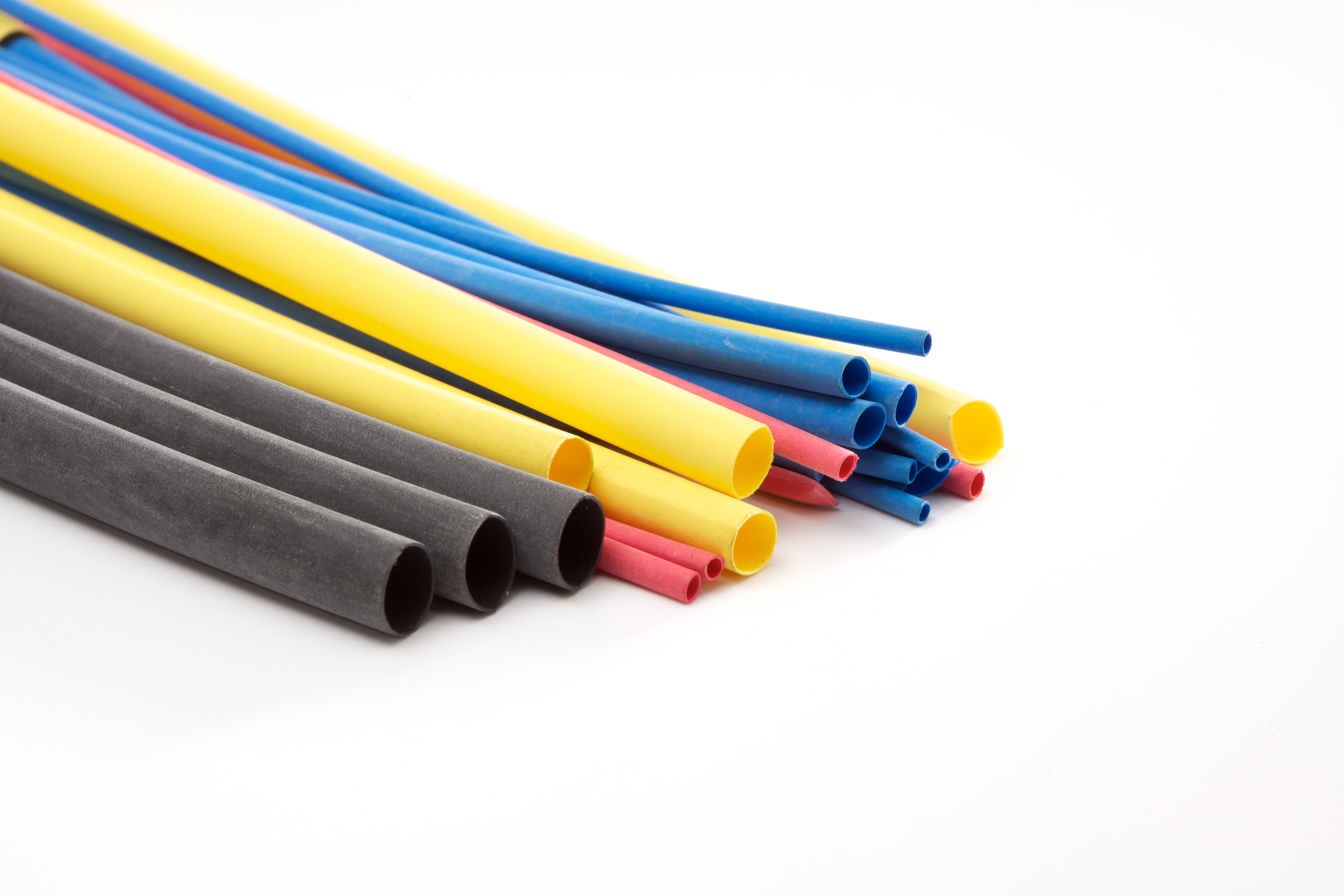

Insulation Durometer Hardness
When selecting insulation materials for a variety of applications, durometer hardness plays a crucial role in determining the material's suitability.Read More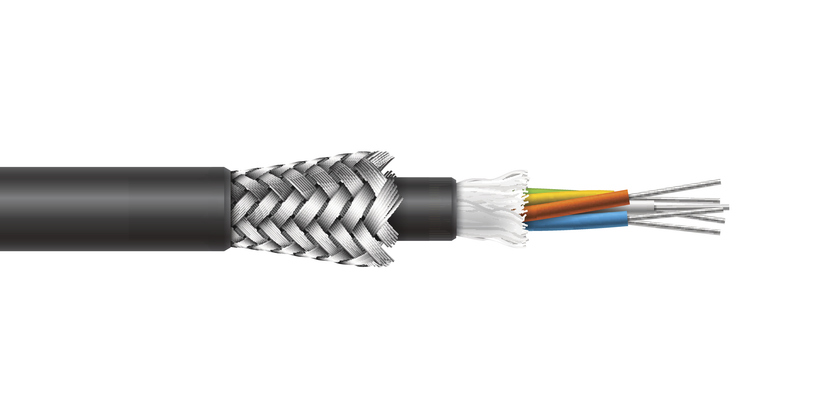
Shielding
Shielding refers to a sheet, screen, foil or braid used to contain electrical energy so that the signal on the cable does not radiate and interfere with signals in other nearby cables and circuitry. Shielding also protects the signal from external interference.Learn More
Cable Sleeving for Wire Management
Cable sleeving is the process of encasing wires in a durable and versatile protective covering. This guide explores everything you need to know about cable sleeving, from selecting the right materials to understanding its applications.Read More